Mobile concrete placing boom rollover
In July 2023, an incident occurred involving the rollover of a boom type concrete pump at a residential construction site. Early investigations showed that the concrete placing boom operator was in the process of packing the plant up. It appears the boom fell onto the house across the street causing substantial damage to the building. Two people were in the house at the time, but fortunately they weren’t injured.
These findings are not yet confirmed, and investigations are continuing into the exact cause.
Safety issues
There are numerous risks associated with the setting-up and packing up of concrete pumping equipment, including mobile concrete pumping booms tipping over and the risk of workers being crushed or run over by the mobile concrete pump itself.
Some issues to be considered when planning for concrete pumping operations include:
- The proximity to overhead powerlines.
- Concrete pumping requirements (including concrete pump selection, concrete delivery, and site access) at the project design stage.
- Ensuring an emergency plan has been prepared for each workplace where concrete pumping work will be done.
- Using additional safety observers depending on the size and complexity of the work.
- Assessing ground support capacity and slope.
- Ensuring enough space is provided to avoid short legging the outriggers - short legging is a practice that should be avoided wherever practicable due to the increased risk of overturning the mobile plant.
Ways to manage health and safety
Effective risk management starts with a commitment to health and safety from those who manage the business. If an incident occurs, you'll need to show the regulator that you’ve used an effective risk management process. This responsibility is covered by your primary duty of care in the Work Health and Safety Act 2011.
Use the hierarchy of controls to help decide how to eliminate and reduce risks in your place of work. The hierarchy of controls ranks types of control methods from the highest level of protection and reliability to the lowest. It’s a step-by-step approach to eliminating or reducing risks. You must work through the hierarchy of controls when managing risks, with the aim of eliminating the hazard, which is the most effective control.
Possible control measures to prevent similar incidents
The Work Health and Safety Regulation 2011 includes specific duties for people conducting a business or undertaking (PCBUs) with management or control of a construction workplace, plant, powered mobile plant, and plant that lifts or suspends loads. If you own concrete pumping plant, you are the person with management or control of that plant and have duties to eliminate or minimise the risks associated with the plant.
Planning and preparation of site
Planning for concrete pumping operations should start as early as possible in the development of any work or project to help eliminate many of the associated health and safety risks. Consultation with all people engaged in the work including the principal contractor, the concrete pumping PCBU, electricity entity, designer, and project manager, is essential.
The Concrete pumping code of practice 2019 (PDF, 1.04 MB) outlines the roles and responsibilities associated with concrete pumping operations including:
- Concrete pump owner - one of the concrete pump owner’s responsibilities is to ensure pads and/or timbers supplied with the concrete pumping equipment will adequately support the plant (the owner may need to seek the advice of a competent person when selecting appropriate materials to support the outrigger feet).
- Concrete pumping equipment operator - before and during concrete pumping operations, the concrete pump operator must in addition to other requirements:
- Complete the daily inspection checklist, including filling out the logbook.
- For mobile concrete placing booms, outriggers should be set according to the manufacturer’s operating instructions for the specific type of mobile concrete pump.
- Monitor the safe use of the concrete pump, concrete delivery lines, and boom.
- In the case of mobile concrete placing booms, monitor the safe support of the carrier, including observing outrigger pads and the ground.
- Be in view of the line hand and monitor the safe delivery of concrete.
Ground conditions
When setting-up a mobile concrete placing boom, the area should be level, capable of supporting the load and free of obstructions, with careful attention paid to the following:
- Precautions should be taken when a concrete placing boom is used in the vicinity of an excavation, the unit should not be positioned over or adjacent to:
- previously disturbed ground that’s been back-filled.
- excavations, trenches, or holes in the ground.
- cellars, basements, or pits.
- inadequately compacted or soft ground.
- If the ground is near an excavation, the pump operator should immediately refer the matter to the principal contractor for re-location to a more stable location.
- When the concrete placing boom is continuously operated in one location, ensure the ground has not compacted to the extent that the boom is more likely to overturn.
- The unit is set up level, and if this is not possible, ensure the incline or angle of the machine does not exceed the manufacturer’s recommendations (refer to operating instruction manual).
- When setting up close to concrete pads/pavement, be aware the ground could be softer due to rain water run-off and/or the ground being disturbed.
Outriggers
- Ensure outriggers are extended in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions when unfolding the boom, during operation, and when folding the boom up (e.g., don’t short leg unless the manufacturer’s operating manual states this can be done).
- Supply members (e.g., timbers) that have a large enough area and won’t flex as packing under the outrigger base plates.
- Ensure the outrigger’s pads are clear of excavations, soft or filled ground, or other obstacles likely to interfere with the safe operation of the machine.
- Ensure the members (e.g., timbers) have sufficient bearing area to support the machine.
- Ensure the outrigger pads do not sink, by making regular checks of suring operation of the plant.
- Timbers, pads, and steel plate should be of dimensions and materials as specified by the concrete pump manufacturer (if the manufacturer has not provided this information, a competent person such as an engineer, should specify the minimum size of the material to be used).
- When setting up outrigger timbers on sloping ground, cut into the ground and set the timbers up so they are level. Don’t lay the timbers on sloping ground as the outrigger feet can slide off the timbers. Don’t bridge the timbers over timbers underneath as this increases the bearing load on the ground (refer Figure 1).
- Ensure outriggers are set up in accordance with the plant manufacturer’s instructions (e.g., see Figure 2).
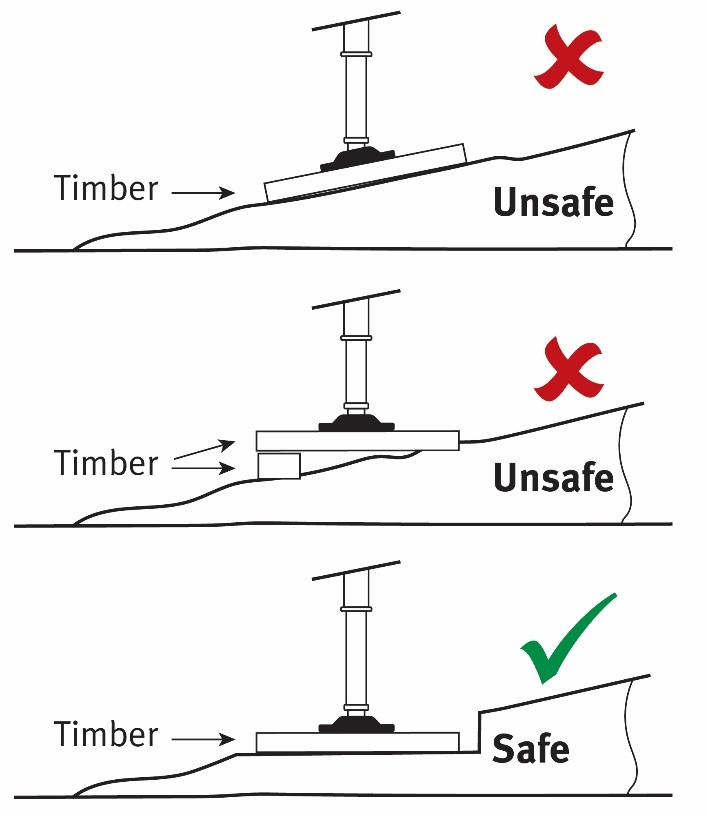
Figure 1: Methods of outrigger base plate support
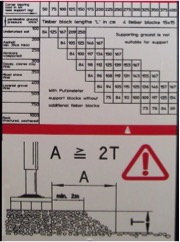
Figure 2: Example of a decal provided by one manufacturer (Putzmeister), as an operator aid. Source: Concrete Pumping code of practice 2019
Ground pressure and outrigger pad area
The ground bearing capacity must be greater than the maximum pressure applied by the mobile plant to the ground to ensure the plant does not sink or overturn. If not, then appropriate control measures, such as increasing the area of the outrigger pads or carrying out earthworks to increase the ground’s bearing capacity are to be implemented.
Some concrete placing boom manufacturers provide information on the maximum force applied by outriggers and the minimum area of outrigger pads to be used. Further guidance on ground bearing capacities can be found in section 4.2.2.4 of the Concrete pumping code of practice 2019 (PDF, 1.04 MB).
Information, training instruction, and PPE
Information, training instruction, or supervision for concrete pumping operations should include:
- The method for inspection and maintenance of concrete pumping equipment.
- Knowledge of the manufacturer's operation and service manuals.
- The work methods to be used in the setting up and safe operation of concrete placement booms and pumps.
- The correct use, care, and storage of tools and equipment to be used, including electrical safety practices.
Supervisors must:
- Ensure only those workers who have received training and instruction are authorised to carry out that work.
- Monitor the work sufficiently to make sure safe work practices are being carried out, including the use of all protection systems and personal protection equipment.
The following items of PPE are required when pumping concrete:
- safety helmets
- eye protection
- safety vest
- rubber safety boots.
The control measures put in place should be reviewed regularly to make sure they work as planned.
Short legging is a practice that should be avoided wherever possible, due to the increased risk of overturning the mobile plant.
At the design and construction stages of the building, designers and specialist contractors should consider that adequate space is available so that mobile plant required as part of the building process, can be safely set up and packed up.
People in control of workplaces and principal contractors should ensure that adequate room is available to enable mobile plant to be set up and packed up safely. This includes, both operation of the mobile plant and ancillary activities, such as cleaning out concrete lines. It may also include obtaining road or footpath closures from the relevant authority.
Sometimes it may be impractical to set up or pack up the mobile plant with outriggers fully extended. This can be due to inadequate planning prior to the arrival of the plant on site, or extraordinary circumstances.
If short legging is implemented ensure:
- The manufacturer's operating manual for the mobile plant states that short legging is permitted. The manufacturer's operating instructions for short legging must state when this practice takes place, including any necessary reduction of the rated capacity of the mobile plant. A copy of the manual is kept with the mobile plant.
- The outriggers are marked with an indicator that shows the extent of the short legging (i.e., marks on the outriggers), or the operator's manual showing how far the outriggers are to be extended (i.e., by diagrams).
- A work method statement has been prepared that shows the operating conditions under which short legging can be used. For concrete placing booms, the work method statement is to include a diagram showing the permissible operating zone of the boom. The work method statement should be provided to the principal contractor's representative (or the person in control, if no principal contractor is required for the job) and the principal contractor is to assess the work method statement to ensure the items above are addressed.
- The stability of a concrete placing boom must be maintained during set up, operation, and pack up.
A typical diagram for short legging of a concrete placing boom is shown below (Diagram 1).
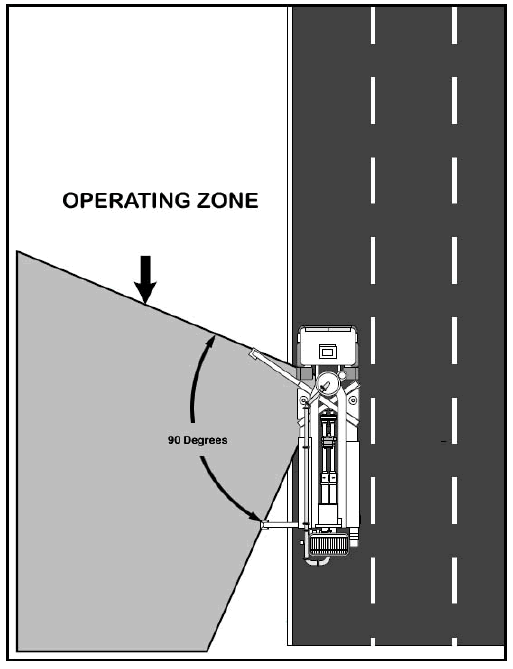
Diagram 1: An example of a diagram for short legging a mobile concrete placing boom. The diagram shows the permitted operating zone. Note: partial road closure obtained, and traffic control procedures implemented.
More information
- Concrete pumping code of practice 2019 (PDF, 1.04 MB)
- Safe support of mobile plant guide (PDF, 3.42 MB)
- Support of mobile plant on outriggers – alert
- Mobile concrete placing boom stability – alert
- Concrete pumping
Have you been affected by a workplace fatality, illness or serious injury?
For advice and support: